AI Learning Roadmap for Beginners — Part 1: Learn, Prompt, Test
AI learning roadmap for beginners: learn generative AI, master prompt engineering, compare ChatGPT vs Claude vs Gemini, and build weekly projects.
Over the past few months, many people have asked me,
“How did you start your AI journey?”
When I began exploring AI, I was a complete beginner with zero experience in AI and came from a no-coding background (for non-coders). I was determined to learn AI because I believed it would be the future.
Unlike just following YouTube videos or reading scattered blogs that don’t provide structured learning, I wanted a systematic approach. So I joined 100xEngineers to get that structured learning experience. I’ve written a complete experience about it in my blog, and I’ll share the link below.
0to100Days of learning GenAI with 100xEngineers : https://akhileshwritings.medium.com/0to100days-of-learning-genai-with-100xengineers-742558730c60
Now, based on my 18 months of journey with AI, I want to share the content and resources I’ve explored that can help you fast-track your learning.
This roadmap is for anyone who wants to apply AI in their work — creators, entrepreneurs, operators — not necessarily to become AI engineers.
You’ll learn how to use AI effectively, experiment with tools, and start automating workflows. A bit of coding helps, but it’s not required.
This series is just getting started! In upcoming articles, we’ll explore:
Real-world AI projects for beginners
Productivity hacks to accelerate your skill-building
Troubleshooting tips, and more
The easiest way to keep growing? Subscribe to get every part delivered to you.
Step 1: How I Understood Generative AI the Right Way
When I started, I jumped straight into using ChatGPT without really knowing what it was doing. It worked for a while, but I couldn’t explain why prompts behaved differently or why outputs varied.
So I went back to the basics — and the course that helped me understand what is Generative AI is below:
🔗 Generative AI for Everyone – deeplearning.ai
It’s simple, non-technical, and explains:
What generative AI is and how it differs from traditional AI
How models like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini generate content
What “foundation models” mean
The risks and opportunities of AI
This course helped me understand how AI works, the basics of AI like transformers, neural network etc.. explained in simple English.
If you’re starting out — do this first. It takes only a couple of hours, but it’ll save you weeks of confusion later.
Actionable:
Schedule 2 hours this week and finish the course.
Note down how models “learn” and what they can’t do — that distinction helps later.
You can also refer to my article on Artificial Intelligence Terminologies to get started and be familiar:
Another good video to check:
Step 2: Learning to Talk to AI (Prompt Engineering for Beginners)
Once I understood the basics, I realised the real skill wasn’t in using the model—it was in communicating with it effectively.
Large language models (LLMs) respond exactly to how you phrase your thoughts. When you learn to prompt correctly, your productivity increases dramatically.
The best resource I found for this was:
I didn’t read everything at once. I focused on a few concepts that made a huge difference in my workflow. But I have completed the whole course and content
a) Understanding LLM Settings
Temperature: controls creativity. High = imaginative, low = factual. For example, Temp 0.8 makes it write like a storyteller; 0.2 makes it precise and dry.
Context window: how much the model can remember. ChatGPT-4 can hold roughly 100 pages of context; once you go beyond that, it forgets earlier parts.
Top P and Top K: decide how random or predictable responses are. I usually leave them default, but knowing they exist helps if results get repetitive.
b) Core Prompting Techniques
I learned these by experimenting daily:
Zero-shot prompting: ask directly, no examples. Ex: “Write a meta description for this page.”
Few-shot prompting: give 2-3 examples to guide tone. Ex: show two tweet samples before asking for a third.
Chain-of-thought prompting: make the model “think step-by-step.” Ex: “Solve this step by step before answering.”
Role-based prompting: assign a persona. Ex: “Act as a UX designer reviewing this app layout.”
ReAct prompting: reason + act, used in agents. Ex: “Analyze this dataset, then summarize key insights.”
Meta-prompting: ask it to critique its own answer. Ex: “Rewrite your answer for clarity and structure.”
JSON prompting: structure the response. Ex: “List 5 startup ideas in JSON with name, tagline, and target user.”
XML-tag prompting: define sections. Ex:
<summary>Write in one paragraph</summary>.
The day I started writing prompts like “Act as…” or “Think step by step,” my results completely changed. That’s when I realized prompting is 80% of AI productivity.
Quick Reference: Settings & Prompting
Step 3: Testing Different Models (LLM Comparison)
Every AI model behaves differently — and I learned this only after using them side by side.
ChatGPT (OpenAI)
Best for: Everyday writing, brainstorming design ideas, and creative productivity.
Experience: ChatGPT remains the most balanced model overall. It excels in generating structured text, refining tone and clarity, and supporting creativity with seamless GPT-image-1 generation.
Ideal for writing workflows, marketing content, and concept visualization.
This has been my go-to application for almost everything related to writing, interpreting,and Projects (Right for Power Users - Will cover a session on using Projects in the next part)
Claude (Anthropic)
Best for: Coding, logical reasoning, and structured analysis.
Experience: Claude feels calm, consistent, and highly reliable for extended coding sessions. It performs exceptionally well when summarizing reports, analyzing data, or writing clear, thoughtful code and documentation.
Gemini (Google)
Best for: Text, image, and video-based creative workflows.
Experience: Gemini shines when combining multiple modalities. It’s great for visual storyboards, presentation planning, and generating creative content that blends narrative with visuals. It’s image generation models like Gemini 2.5 Flash is awesome along with their Veo3 for Video Generation
Grok (xAI)
Best for: Social media insights and tone adaptation.
Experience: Grok is tuned for the X (Twitter) ecosystem. It’s effective at analyzing trends, understanding online sentiment, and replicating conversational or witty tones. A powerful companion for creators, marketers, and analysts working with real-time social data.
When I started running the same prompt across all models, I understood their personalities. Claude reasons deeply; Gemini visualizes beautifully; ChatGPT formats perfectly; Grok sounds human.
Try this yourself:
“Explain how small businesses can use AI to improve customer support.”
You’ll see how each model interprets it differently — that’s where learning happens.
Step 4: Observe, Analyse, and Iterate
I learned more by observing AI than by reading tutorials. I took a conversational approach — constantly testing, analyzing, and iterating in real-time.
Here’s how I did it:
I’d give the same task to three different models (ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini)
Then I’d analyse each response — which one understood better, which gave more useful output
Finally, I’d iterate within each conversation — refining prompts, testing variations, observing changes
Within weeks, patterns became clear. I knew which models excelled at what, and how to phrase prompts for better results.
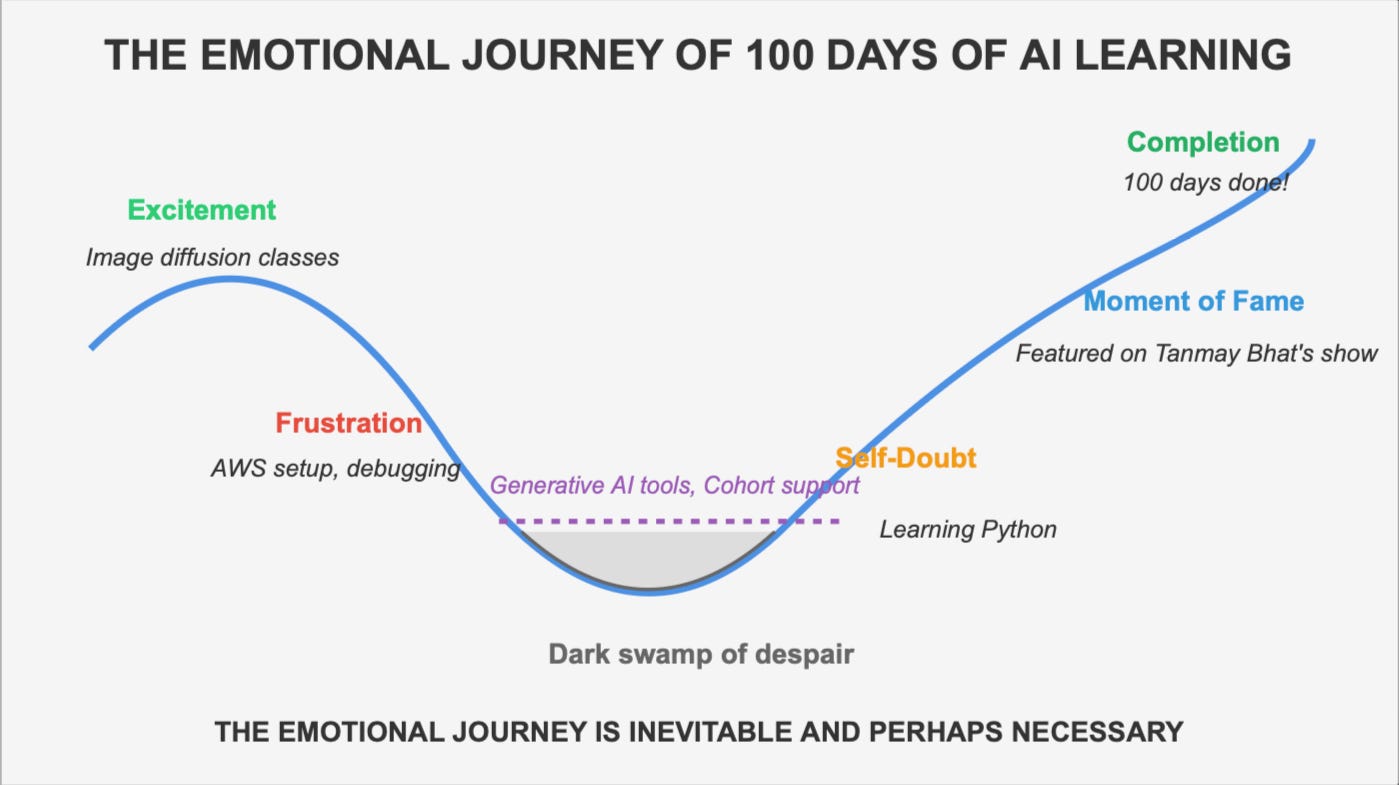
AI learning isn’t about memorising terms or keeping formal notes — it’s about developing an intuition through continuous observation, comparison, and iteration.
Step 5: Building Consistency (and Doing Real Projects)
In the beginning, I focused too much on writing tasks. But the real power of AI starts when you use it to build, visualize, and automate.
Here’s how you can structure your practice :
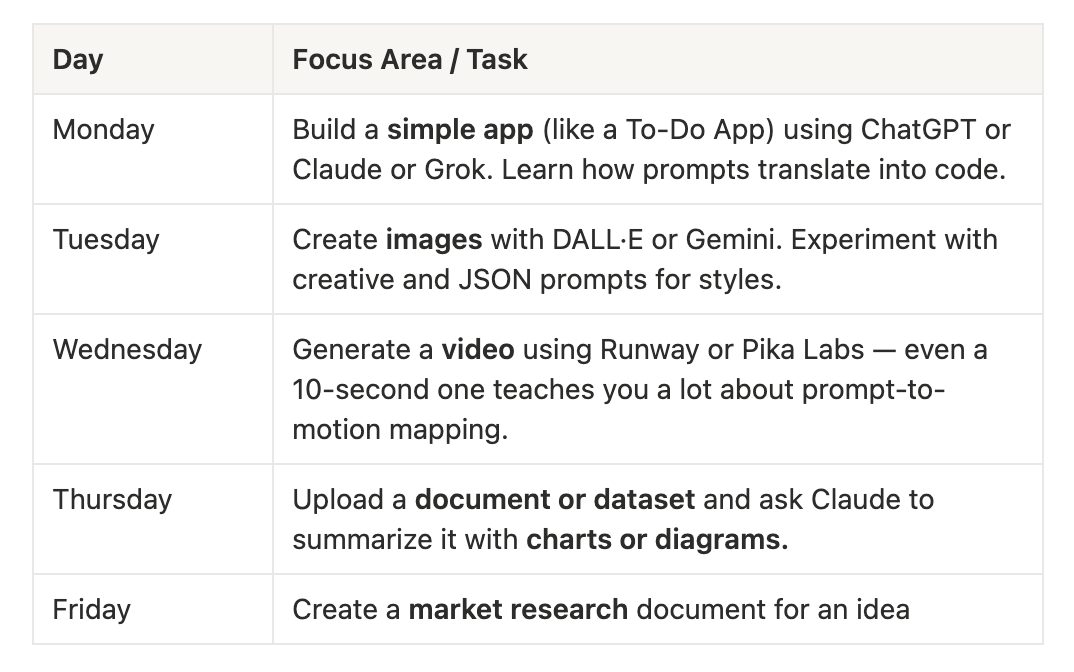
Weekly AI Practice Plan
Monday – Build a Simple App
Start the week by creating a basic app, such as a To-Do List application, using tools like ChatGPT, Claude, or Grok. Focus on understanding how natural language prompts translate into executable code. Observe how each model handles logic, UI components, and syntax suggestions differently.
Tuesday – Explore Image Generation
Use DALL·E or Gemini to create images based on your ideas. Experiment with creative prompts and JSON-based style prompts to see how structure, lighting, and tone can be controlled. This exercise builds a foundation for visual storytelling and helps you understand prompt precision.
Wednesday – Generate a Short Video
Try making a short, 10-second video using Runway or Pika Labs. Even a small project teaches a lot about prompt-to-motion mapping—how textual instructions translate into camera angles, movement, and scene flow. Focus on timing, continuity, and visual coherence.
Thursday – Work with Documents and Data
Upload a document or dataset and ask Claude to summarize it visually using charts or diagrams. Learn how structured analysis, summarization, and visualization can be automated, and experiment with different prompt styles to get more insightful outputs.
Friday – Conduct Market Research
Wrap up the week by creating a market research document for any business or product idea. Use AI to identify competitors, target users, and unique differentiators. Combine text generation with visuals and structured tables to produce a professional-quality research brief.
These small projects helped me move beyond text generation. They showed me how AI can assist in coding, design, storytelling, and workflow automation — all without deep technical skills.
Step 6: Explore the Ecosystem
Start exploring different LLM Chats. Listing down few tools that you must know and try
Core AI Tools
Different model & tools to explore :
Text Generation: Mistral, DeepSeek, Llama (open-source)
Image Generation: DALL-E, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, Flux
Video Generation: Sora, Runway, Luma Dream Machine , Kling,
Audio Generation: ElevenLabs, Suno, Udio
Try to generate Text, Image, and Videos in all the models.
Communities & Creators I Follow
Make your social media feed show content around AI. Just follow few AI creators on X.com or see few AI videos on Youtube and then they will keep you bombarding with all the AI content getting created.
These channels helped me understand how people are actually using AI:
Riley Brown: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCMcoud_ZW7cfxeIugBflSBw
Brendan Jowett: https://www.youtube.com/@brendanautomation
AICodeKing: https://www.youtube.com/@AICodeKing
3Blue1Brown: https://www.youtube.com/@3blue1brown ( A must for anyone who wants to learn how AI fundamentally works)
Lenny’s Podcast: https://www.youtube.com/@LennysPodcast
IBM Channel: https://www.youtube.com/@IBMTechnology (Wonderful Content on AI)
On X.com (Twitter):
Andrej Karpathy: https://x.com/karpathy
Aadit Sheth: https://x.com/aaditsh
Akshay: https://x.com/akshay_pachaar
elvis: https://x.com/omarsar0
Ray Fernando: https://x.com/RayFernando1337
Riley Brown: https://x.com/rileybrown_ai
Y-Combinator: https://x.com/ycombinator
Where to Discover New Models
There are platforms where you would see many open source models hosted:
Hugging Face — hosts thousands of open-source AI models.
Replicate — run models for text, image, audio, and video without setup.
Fal — run models for text, image, audio, and video without setup.
We’ll cover how to use these in later parts — but for now, just bookmark them.
Wrapping Up Part 1
So that’s how I began my journey — from not knowing how models work to using them to write, build apps, generate visuals, and automate workflows.
If you complete these same steps — the course, prompting guide, model testing, and a few real-world exercises — you’ll have a strong foundation.
In Part 2, we’ll delve deeper: connecting your models to tools through MCP (Model Context Protocol) and learning to utilise ChatGPT projects for enhanced productivity, such as Computer Use Agents and Study & Learn mode.
That’s where you move from just using AI to making it work for you.
What’s your biggest challenge in learning AI? Drop your answer in the comments or reply—and I’ll address it in future articles.
Updating my Part 2 & Part 3 articles:






I resonate with what you wrote about needing a systematic aproach. How do you see the role of traditional coding skills fitting into this application-focused AI journey long-term? This roadmap is incredibly insightful.